|
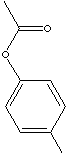
Para Cresyl Acetate
CAS NO. 140-39-6
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
p-CRESYL ACETATE
EINECS NO. 205-413-1
FORMULA C9H10O2
MOL WT. 150.18
H.S. CODE2916.35
DERIVATION TOXICITY
SYNONYMS Acetic acid, p-tolyl ester; p-Acetoxytoluene;
p-Cresylic acetate; p-methyl phenyl acetate; p-tolyl acetate;
4-Acetoxytoluene; p-Cresol acetate;
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
PHYSICAL STATE clear liquid
MELTING POINT
BOILING POINT 210 - 211 C
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 1.04 - 1.05
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
Insoluble
pH
VAPOR DENSITY
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0
FLASH POINT
STABILITY Stable under ordinary conditions.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS
Cresols are methyl substituted phenols at relative to the hydroxyl
group, ortho-, meta-, and para-cresol. There are three structural
isomers. The names of the three compounds indicate which of the
hydrogens on the benzene ring portion of the molecule have been
replaced. They are obtained from coal tar or petroleum. Because the
boiling points of these three compounds are nearly the same, a
separation of a mixture of the three into its pure components is
impractical. They are highly flammable and are soluble in water,
ethanol, ether, acetone and alkali hydroxides. T
The mixture of cresols obtained from coal tar is called cresylic acid,
an important technical product used as a disinfectant and in the
manufacture of resins and tricresyl phosphate. Cresylic acid also refs
to the mixture of phenols containing varying amounts of xylenols,
cresols, and other high-boiling fractions, but not more than 5 percent
phenol. Commercial cresols are prepared in a wide range of grades and
purities to meet the user's requirements. It is a liquid from clear to
brown and is toxic to animals including human. It is corrosive and is a
more powerful disinfectant and antiseptic than phenol. The primary use
is for sterilizing as disinfectants and deodorizers, and pesticides.Its
solution is used as household cleaners as a disinfectant. Creosote is a
mixture of guaiacol, creosol and other phenolic compounds obtained from
wood tar (mainly beech) by distillation mostly between 203 and 220 C. It
is a clear to yellowish, oily liquid; insoluble in water, soluble in
methanol, acetone. It is used as a wood preservative. It is used as an
external antiseptic, expectorant, gastric sedative, deodorant, and as an
antiseptic parasiticide veterinary use in the form of creosote
carbonate.
It is used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and vanillin. Each
cresols are used as solvents or disinfectants and as useful as raw
materials for various chemical products icluding disinfectants,
synthetic resins, fragrances, pigments, drugs, antioxidants, dyes, UV
absorbers, and pesticides. Cresols undergo electrophilic substitution
reactions such as chlorination, bromination, sulfonation and nitration
at the vacant position. They also undergo condensation reactions with
aldehydes, ketones or dienes. O-cresol is a starting material for the
synthesis of herbicides such as 4,6-dinitro-o-cresol (DNOC) and
2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid (MCPA). Meta-cresol is used in the
manufacture of explosives. Meta and para-cresol are used in
phenol-formaldehyde resins and are converted to tricresyl phosphate used
as a plasticizer and gasoline additive and antioxidants such as
di-tert-butylcresols (BHT). Ortho- and para-cresols are used in the
production of lubricating oils and motor fuels.
Acetate is the ester that an organic group replaces a hydrogen atom in
-OH group of acetic acid through reaction (typically condensation) with
alcohols. Condensation is the reaction in which two molecules having -OH
groups are joined with eliminating a water molecule from their -OH
groups. The term acetate is also for the salt that one or more of the
hydrogen atoms of acetic acid are replaced by one or more cations of the
base, resulting in a compound containing the negative organic ion of
CH3COO-. Organic acetates are good solvents for a broad range of resins
as they are miscible with almost all common organic liquids. Due to
their powerful solvency, high volatility and mild odor, acetates are
widely used in the manufacture and in the processing of paints,
coatings, adhesives, and printing industry. They have a very low
solubility in water and used as extraction solvents for fine chemicals
particularly for certain antibiotics. They are also used as components
of aroma. They are used as chemical intermediate to manufacture
pharmaceuticals, synthetic flavorings, cleaners, and other organic
compounds.
p-Cresyl Acetate is used in formulating microbiocides and disinfectants.
It is used in perfumeries and flagrances.
APPEARANCE
clear liquid
CONTENT
98.0% min
ACID VALUE 1.0 max (mg KOH/g)
TRANSPORTATION
PACKING 200kgs in drum
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are used
in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to help
you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of hazards,
not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS). MSDS
forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many chemical
suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL Safety web site,
where this page was hosted, has been copied onto many other sites,
often without permission. If you have any doubts about the veracity
of the information that you are viewing, or have any queries, please
check the URL that your web browser displays for this page. If the
URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium Benzoate.htm/" the page is
maintained by the Safety Officer in Physical Chemistry at Oxford
University. If not, this page is a copy made by some other person
and we have no responsibility for it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive Drug
Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the federal
U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation,
possession, use and distribution of certain substances is regulated.
The Act also served as the national implementing legislation for the
Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs |
|
|
|
|







