|
Methyl Tyramine
CAS NO. 55-81-2
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CAS NO. 55-81-2
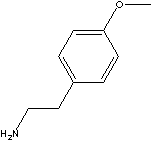
O-METHYL TYRAMINE
EINECS NO. 200-245-5
FORMULA C9H13NO
MOL WT. 151.21
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
SYNONYMS 4-Methoxyphenethylamine;
p-Methoxyphenethylamine; p-Methoxyphenylethylamine; Homoanisylamine;
2-(p-Methoxyphenyl)ethylamine;
2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)ethylamine; 4-Methoxy-beta- phenylethylamine;
4-Methoxy-2-phenethylamine; 4-Methoxybenzeneethanamine;
4-Methoxyphenethylamine; 4-Methoxyphenylethylamine;
2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)ethanamine; p-metoxifenetilamina (Spanish);
p-méthoxyphénéthylamine
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
PHYSICAL STATE pale yellow clear liquid
MELTING POINT
BOILING POINT 138 - 140 C at 20 mm Hg
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 1.03 - 1.035
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
pH
VAPOR DENSITY
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
1.538
FLASH POINT
STABILITY
Stable under ordinary conditions
APPLICATIONS
Tyramine [4-(2-Aminoethyl)phenol] is a monoamine compound of 4-hydroxy
phenethylamine. It is derived from tyrosine, an amino acid (protein
building block) that is the precursor of norepinephrine. It, through its
effect on neurotransmitters, may affect several health conditions,
including Parkinson's disease, depression, alcohol withdrawal support,
and Phenylketonuria. (PKU). Tyramine is naturally found in plant and
animal tissues, certain cheeses and ergot or produced synthetically. It
is metabolized by monoamine oxidase. Tyramine or its derivatives can be
used in pharmaceutical industry such as:
* Sympathomimetic or adrenergic drugs themselves or intermediate of
them.
* Intermediate for bezafibrate used in the treatment of high cholesterol
levels.
* Determination of peroxide activity in the fluorescence enzyme
immunoassay for insulin.
* False transmitter.
Tryptamine [3-(2-Aminoethyl)indole] is a biologically important
monoamine compound derived by the decarboxylation of tryptophan, indole
side chain amino acid. In addition to its function to build the
structure of protein, tryptophan is a precursor for neurotransmitter and
neurohormone. Tryptamine (biological monoamine) effects vasoconstriction
by causing the release of norepinephrine at postganglionic nerve
endings. Several mental disorders and health conditions are explained as
due to either an excess or deficiency of monoamines. There are many
natural tryptamines in both animal and plant as well as synthetics
modified by chemical constituents and substituted at appropriate
positions in the motif. Common tryptamine class compounds include;
* Bufotenine (CAS #: 487-93-4): (5-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine,
pressor agent, epinephrine-like.
* DMT (CAS #: 61-50-7): N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, a psychedelic and
hallucinogenic.
* Luzindole (CAS #: 117946-91-5): N-Acetyl-2-benzyltryptamine
* Melatonin (CAS #: 73-31-4, 8041-44-9): N-Acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine,
biological clock hormone.
* Psilocin: 4-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine.
* Psilocybin (CAS #: 520-52-5): 4-Phosphoryloxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine,
a hallucinogenic.
* Serotonin (CAS #: 50-67-9): 5-Hydroxytryptamine, a vasoconstrictor.
* Sumatriptan( CAS #: 103628-46-2)
4-Hethylaminosulfonyl-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, selective serotonin
antagonist used in the treatment of migraine headache.
SPECIFICATION
APPEARANCE
pale yellow clear liquid
ASSAY
99.0% min
TRANSPORTATION
PACKING 200kgs in fiber drum
HAZARD CLASS 8 (Packing Group: III)
UN NO. 2735
OTHER INFORMATION
Hazard Symbols: C, Risk Phrases: 34, Safety Phrases: 26-36/37/39-45
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CATECHOLAMINE
Catecholamine: a group of naturally occurring sympathomimetic amines
that have important physiological functions within the body as
neurotransmitters in the central nervous system and hormones in the
blood circulation. Catecholamines are biogenic amines considered as
sympathomimetic drugs; They are characterized by a catechol group [The
ortho (1,2) isomer of dihydroxybenzene] to which is attached an amine
group (the aromatic portion of whose molecule is catechol, and the
aliphatic portion an amine). The most abundant catecholamines in the
body are epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and
dopamine. They are derived from the tyrosine, an amino acid (protein
building block) that is the precursor of norepinephrine. (The prefix
nor- describes normal structure which has no branched chain of carbon
atoms. In case of norepinephrine, it has one less methylene group than
its homologue, epinephrine.) Catecholamines belong to a broader class of
compounds called phenethylamines which contain structurally amino acid,
phenylalanine and tyrosine. Phenethylamine is a backbone for the
compounds which take roles of alkaloids as well as hormones and
neurotransmitters in nature. Amphetamine is the substituted
phenethylamine by methyl group at alpha position. It is a synthetic drug
used as a diet suppressant and to treat narcolepsy and ADHD (attention
deficit hyperactivity disorder). But amphetamines can produce severe
psychological dependence, including cardiac irregularities and gastric
disturbances. Chronic use often results in extreme exhaustion and
malnutrition.
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are used
in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to help
you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of hazards,
not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS). MSDS
forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many chemical
suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL Safety web site,
where this page was hosted, has been copied onto many other sites,
often without permission. If you have any doubts about the veracity
of the information that you are viewing, or have any queries, please
check the URL that your web browser displays for this page. If the
URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium Benzoate.htm/" the page is
maintained by the Safety Officer in Physical Chemistry at Oxford
University. If not, this page is a copy made by some other person
and we have no responsibility for it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive Drug
Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the federal
U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation,
possession, use and distribution of certain substances is regulated.
The Act also served as the national implementing legislation for the
Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs |
|
|
|
|







