
Cefoperazone Sodium
CAS NO. 62893-19-0 (Base)
62893-20-3 (Sodium)
CEFOPERAZONE SODIUM
EINECS NO. 263-749-4(Base)
62893-19-0 (Sodium)
FORMULA C25H27N9O8S2·Na
MOL WT. 667.65
CLASSIFICATION
ANTIBOITICS / CEPHALOSPORINS /
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
PHYSICAL STATE White to slightly yellowish crystalline powder
MELTING POINT
BOILING POINT
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
SOLUBILITY IN WATER Freely soluble (practically insoluble in ether)
pH 4.5 - 6.5
STABILITY Stable under ordinary conditions.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Cephalosporin: any of a group of broad-spectrum derived from species of
fungi of the genus Cephalosporium and are related to the penicillins in
both structure and mode of action but relatively penicillinase-resistant
antibiotics. These antibiotics have low toxicity for the host,
considering their broad antibacterial spectrum. They have the active
nucleus of beta-lactam ring which results in a variety of antibacterial
and pharmacologic characteristics when modified mainly by substitution
at 3 and 7 positions. Their antibacterial activities result from the
inhibition of mucopeptide synthesis in the cell wall.
They are widely used to treat gonorrhea, meningitis, pneumococcal,
staphylococcal and streptococcal infections. The cephalosporin class of
antibiotics is usually divided into generations by their antimicrobial
properties. Three generations of cephalosporins are recognized and the
fourth has been grouped.
Each newer generation of cephalosporins has broader range of activity
against gram-negative organisms but a narrower range of activity against
gram-positive organisms than the preceding generation. The newer agents
have much longer half-lives resulting in the decrease of dosing
frequency. Accordingly, the third-generation cephalosporins can
penetrate into tissues well, and thus antibiotic levels are good in
various body fluids. Second-generation cephalosporins have broader
spectrums of activity against gram negative coverage but less active
against gram-positive organisms than first-generation agents. T
Cefoperazone sodium is a semi-synthetic 3rd generation cephalosporin
effective against a wide range of aerobic and anaerobic gram-positive
and gram-negative bacteria. It is a white to pale yellow crystalline
powder; soluble in water, methanol; slightly soluble in dehydrated
alcohol; insoluble in acetone, ethyl acetate, ether. Chemical
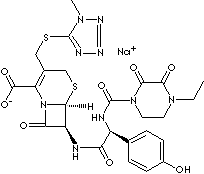
designation is
[6R-[6a,7b(R')]]-7-[[[[(4-ethyl-2,3-dioxo-1-piperazinyl)carbonyl]
amino](4-hydroxyphenyl) acetyl]amino]-3
-[[(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo- 5-thia-1-azabicyclo
[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, monosodium salt.
Chemistry - A third generation cephalosporin, cefoperazone sodium
contains a piperazine side chain giving it antipseudomonal activity. It
occurs as white, crystalline powder and is freely soluble in water and
poorly soluble in alcohol. At room temperature, cefoperazone sodium has
a maximum solubility in compatible IV solutions of 475 mg/ml (at
concentrations >333 mg/ml vigorous and prolonged shaking may be
required). Reconstituted solutions of the drug have a pH from 4.5 - 6.5.
One gram contains 1.5 mEq of sodium.
Storage/Stability/Compatibility - The sterile powder for injection
should be stored at temperatures less than 25°C and protected from
light. Once reconstituted, solutions do not need to be protected from
light.
Uses/Indications - Cefoperazone is used to treat serious infections,
particularly against susceptible Enterobacteriaceae not susceptible to
other less expensive agents or when aminoglycosides are not indicated
(due to their potential toxicity).
Adverse Effects/Warnings - Cefoperazone is a relatively safe agent.
Rarely, hypersensitivity reactions could potentially occur in animals.
Because of its thiomethyltetrazole side-chain it may also rarely cause
hypoprothrombinemia. Diarrhea secondary to changes in gut flora have
been reported.
|
|








