
|
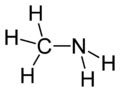
Methylamine
|
|
Methylamine IUPAC name :
aminomethane
Other names : monomethylamine MMA
Identifiers
CAS number : [74-89-5]
Molecular formula : CH5N
Molar mass : 31.06 g mol−1
Appearance : Colorless Gas
Density : d40.699 (−10.8 °C) / 0.902 g/cm³, 40w/w% in water
Melting point : −94 °C (179.15 K)
Boiling point : −6 °C (267.2 K)
Solubility in water : 108 g/100 mL (20 °C)
Acidity (pKa) : 10.64 (value for protonated amine, pKaH)
Basicity (pKb) : 3.36
Viscosity : 0.23 cP at 0 °C
Structure : Molecular shape tetrahedral
Dipole moment : 1.31 D (gas)
R-phrases : 11-36/37 (40% solution in water)
Flash point : 8 °C |
Methylamine is the organic compound
with a formula of CH3NH2. This colourless gas is a derivative of
ammonia, wherein one H atom is replaced by a methyl group. It is the
simplest primary amine. It is sold as a solution in methanol, ethanol,
THF, and water, or as the anhydrous gas in pressurized metal containers.
Industrially methylamine is sold in its anhydrous form in pressurized
railcars and tank trailers. It has a strong odour similar to fish.
Methylamine is used as a building block for the synthesis of many other
commercially available compounds.
Production
Methylamine is prepared commercially by the reaction of ammonia with
methanol in the presence of a silicoaluminate catalyst. Dimethylamine
and trimethylamine are coproduced; the reaction kinetics and reactant
ratios determine the ratio of the three products.
Applications
Methylamine is a good nucleophile as it is highly basic and unhindered.
Its use in organic chemistry is pervasive. Some reactions involving
simple reagents include: with phosgene to methyl isocyanate, with carbon
disulfide and sodium hydroxide to the sodium methyldithiocarbamate, with
chloroform and base to methyl isocyanide and with ethylene oxide to
methylethanolamines.
Representative commercially significant chemicals produced from
methylamine include the pharmaceuticals ephedrine and theophylline, the
pesticides carbofuran, carbaryl, and metham sodium, and the solvents
N-methylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone. The preparation of some
surfactants and photographic developers require methylamine as a
building block.
Liquid methylamine can be used as a solvent analogous to liquid ammonia.
It shares some of the properties of liquid ammonia, but is better for
dissolving organic substances, in the same way that methanol is better
than water.
Biological chemistry
Methylamine arises naturally as the result of putrefaction
Putrefaction
Putrefaction is the decomposition of animal proteins, especially by
Anaerobic organism, described as putrefying bacteria. Decomposition is a
more general process and is a substrate for methanogenesis
Methanogenesis
Methanogenesis or biomethanation is the formation of methane by microbes
known as methanogens. Organisms capable of producing methane have been
identified only from the Kingdom Archaea, a group Phylogenetics distinct
from both eukaryotes and bacteria, although many live in close
association with anaerobic bacteria. It serves as a buffering agent.
Buffering agent
A buffering agent adjusts the pH of a solution. The function of a
buffering agent is to drive an acidic or basic solution to a certain pH
state and prevent a change in this pH in the lumen of the chloroplast
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryote
organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy
to conserve Thermodynamic free energy in the form of Adenosine
triphosphate and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes
called photosynthesis in plants, effectively siphoning off protons that
are heading for ATP synthase
An ATP synthase is a general term for an enzyme that can synthesize
adenosine triphosphate from adenosine diphosphate and inorganic
phosphate by using some form of energy.
.
Safety
In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 , or LCt50 of a toxic
substance or radiation is the Dose required to kill half the members of
a tested population (mouse) is 2400 mg/m3. Methylamine is also
controlled as a List 1 substance by the United States Drug Enforcement
Agency (DEA)
Drug Enforcement Administration
The Drug Enforcement Administration is a United States Department of
Justice law enforcement agency tasked with combating War on Drugs Not
only is the DEA the lead agency for domestic enforcement of the drug
policy of the United States , it also has sole responsibility for
coordinating and pursuing U.S. lists methylamine as a precursor (to
methamphetamine.
Methamphetamine is a stimulant and sympathomimetics psychoactive drug.
It is a member of the family of phenylethylamines. The levorotary
levomethamphetamine is an over-the-counter drug and used in Vicks
Inhalers for nasal decongestion and does not possess the Central nervous
system activity of dextro or racemic methamphetamine.
 Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as
those that are used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and
are important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your country
government laws /control substance ACT. Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as
those that are used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and
are important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your country
government laws /control substance ACT.
Note /Government Notification:
N/A
|
|









