|
 Active Ingredients: Active Ingredients:
• BENZYL PENICILLIN 600 mg (1 Mu) INTRAMED Powder for Injection
BENZYL PENICILLIN 3,0 g (5 Mu) INTRAMED Powder for Injection
 COMPOSITION:
COMPOSITION:
|
1. |
Benzyl penicillin
600 mg per vial, as the sodium salt
|
|
2. |
Benzyl penicillin 3,0 g per vial, as the
sodium salt.
Buffered with 3,0% m/m sodium citrate |
PHARMACOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION:
A 20.1.2 Penicillins.
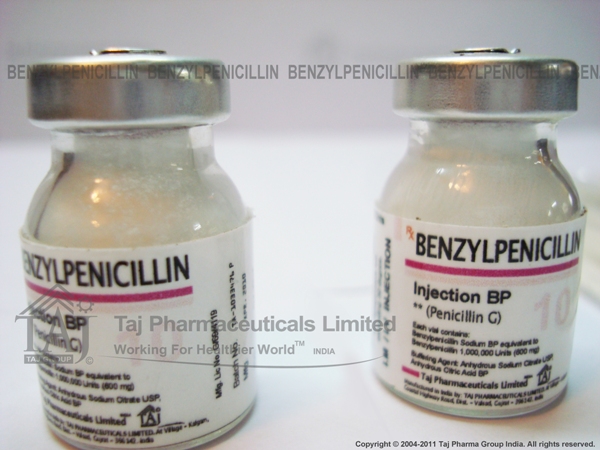
 PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION:
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION:
The cell walls are essential for normal growth
and development of bacteria. Peptidoglycan is the
heteropolymeric component of the cell wall providing rigid
mechanical stability. The action of the beta-lactam antibiotics
is involved in the third stage of cell membrane cross-link
formation, namely the transpeptidation reaction. The terminal
glycine residue of the pentaglycine bridge is linked to the
fourth residue (D-alanine) releasing the fifth residue (also D-alanine)
and this step is inhibited by the beta-lactam antibiotics. The
transpeptidase is probably acylated by penicillin. Various
penicillin binding proteins (transpeptidases and
carboxypeptidases) are associated with the bacterial cell
membrane and beta-lactam antibiotics bind tightly to them. The
penicillin binding proteins vary from one bacterial species to
another and in their affinity for different antibiotics. The
morphological changes brought about are dependant on the
antibiotic, its concentration and the microbe. As the
concentration is increased, growth is inhibited, bulges form and
lysis follows. Resistant strains (containing no autolysins) will
not lysate and different type of antibiotics are to be used.
Bacterial resistance may be because of:
|
1) |
enzymatic structural differences (natural or because of
mutation); |
|
2) |
inability of antibiotic to permeate its site of action; |
|
3) |
enzymatic destruction by beta lactamases or
penicillinases. |
Its
activity is also influenced by:
|
a) |
density of bacterial population and the age of an
infection; |
|
b) |
these antibiotics are most active against bacteria in
the logarithmic phase of growth and have little effect
on bacteria in the lagphase; |
|
c) |
bacteria that survive inside viable host cells are
protected; |
|
d) |
low
pH or oxygen tension activate the antibiotics. |
After intramuscular injection peak plasma
concentrations are reached within 15 to 30 minutes. The
penicillin G halflife is about 30 minutes. This may be prolonged
with Probenecid. Benzyl penicillin is distributed in the body
about 50% in the total body water, 90% in the blood is in the
plasma and 65% is reversibly bound to plasma albumin.
Significant amounts appear in liver, bile, kidney, joint fluid,
lymph, intestines and semen. Therapeutically effective
concentrations can be attained in the CSF if the meninges are
acutely inflamed. It is rapidly excreted by the kidneys.
 INDICATIONS:
INDICATIONS:
Benzyl
penicillin is highly active against gram-positive cocci and is
similar to that of penicillin V in aerobic gram-positive
micro-organisms. It is five to ten times more active against
gram-negative micro-organisms.
|
1. Gram-positive Cocci |
Diseases |
|
1st Choice |
Dose Mu (Mega-units) |
Duration of Therapy |
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
Abscesses, Bacteremia, Endocarditis, Pneumonia. |
Penicillin G
sensitive |
Penicillin G |
10
to 20 mega-units per day |
3 to
5 days |
|
|
Meningitis, Osteomyelitis, Cellulitis, Other. |
Penicillin G resistant |
A Penicillinase
resistant Penicillin |
. |
. |
|
|
|
Methicillin resistant |
Vancomycin |
. |
. |
|
Streptococcus pyogenes |
Pharyngitis, Scarlet fever, Otitis media, Sinusitis,
Cellulitis, Erysipelas, Pneumonia, Bacteremia,
Other systemic infections |
|
Penicillin G |
10
to 20 Mu per day in 4 to 6 portions or continuous
infusion |
2 to
4 weeks |
|
|
|
|
Penicillin V |
500
mg every 6 hours |
10 days |
|
Streptococcus (viridans group) |
Endocarditis, Bacteremia. |
|
Penicillin G + Streptomycin or Gentamicin |
6 to
10 Mu per day -I.V. & Streptomycin 500 mg I.M. twice
daily. |
2 weeks |
|
r |
|
|
|
Some
prefer Pen. G. alone |
4 weeks |
|
Streptococcus agalactia
(B group) |
Septicemia
Meningitis |
|
Ampicillin or Penicillin G & Amino-glycoside |
150 000 to 250 000 units per kg per day parenterally |
|
|
Streptococcus faecalis (enterococcus) |
Endocarditis |
|
Penicillin G & Gentamicin or Streptomycin |
20
Mu daily -I.V. & Streptomycin 500 mg I.M. every 12 hours
or Gentamycin 1 mg/kg every 8 hours |
4 to
6 weeks |
|
|
Urinary tract infection, Bacteremia |
|
Ampicillin or Penicillin G |
10
to 20 Mu I.V. |
2 weeks |
|
Streptococcus bovis |
Endocarditis, Urinary-tract infection, Bacteremia. |
|
Penicillin G & Streptomycin or Gentamicin |
10
to 20 Mu I.V. |
2 to
4 weeks |
|
Streptococcus (anaerobic species) |
Bacteremia, Endocarditis, * Brain and other abscesses,
Sinusitis. |
|
Penicillin G |
10
to 20 Mu I.V.
*20 Mu daily & Chloramphenicol 2 - 4 g daily I.V. or
metronidazole 2 - 4 g daily I.V. |
At
least 2 weeks |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) |
Pneumonia, Endocarditis, Arthritis Sinusitis, Otitis. |
|
Penicillin G |
10
to 20 Mu daily I.V. |
At
least 2 weeks |
|
|
|
|
|
If
there is bone infection, prolong therapy |
To
at least 4 weeks |
|
|
Meningitis |
|
Penicillin G |
20
to 40 Mu daily by constant I.V. drip or divided into
boluses every 2 - 3 hours |
14 days |
|
2. Gram-negative Cocci |
Diseases |
|
1st Choice |
Dose |
Duration of therapy |
|
Neisseria gonorrhoea (gonococcus) |
Genital infections |
Penicillin sensitive |
Ampicillin or Amoxicillin Penicillin G
A tetracycline |
Only
longacting Pen. G plus Probenecid |
|
|
|
|
Penicillinase producing |
Spectinomycin |
|
|
|
Arthritis-dermatitis syndrome |
|
Ampicillin or Amoxicillin Penicillin G |
10 Mu
daily -I.V |
3 days |
|
|
|
|
|
followed by ampicillin or Amoxicillin given orally |
5 -
7 days |
|
Neisseria meningitidis |
Meningitis, Bacteremia. |
|
Penicillin G |
20-24 Mu daily by constant I.V. drip or divided into
boluses given every 2 - 3 hours |
14 days |
|
|
Carrier state |
|
Rifampicin |
. |
. |
|
3. Gram-positive Bacilli |
Disease |
1st Choice |
Dose Mu (million units) |
Duration of therapy |
|
Bacillus anthracis |
"Malignant pustule", Pneumonia |
Penicillin G |
10
to 20 Mu |
12 days |
|
Corynebacterium diphtheria |
Pharyngitis, Laryngotracheitis, Pneumonia, Other local
lesions |
Penicillin G (Eliminates the carrier state) |
2-3 Mu
daily
in divided doses |
10-12 days |
|
|
Carrier State |
Erythromycin |
. |
. |
|
Corynebacterium aerobic and anaerobic (diphtheroids) |
Endocarditis, Infected foreign bodies. |
Penicillin G and an Aminoglycoside. Vancomycin |
2 to
3 Mu dailyin divided doses |
10-12 days |
|
Listeria monocytogenes |
Meningitis, Bacteremia
*Endocarditis |
Ampicillin or Penicillin G and an Aminoglycoside |
15
to 20 Mu daily parenterally |
At
least 2 weeks
* not less than 4 weeks |
|
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae |
Erysipeloid |
Penicillin G |
When
endocarditis present 2-20 Mu daily |
4 to
6 weeks |
|
Clostridium perfrigens and other species |
Gas
Gangrene |
Penicillin G |
10-20 Mu daily, parenterally
300 mg every 6 hours in prophylactic |
7 days |
|
Clostridium tetani |
Tetanus |
Penicillin G |
To
eradicate vegetative bacterial forms |
. |
|
4. Gram-negative Bacilli |
. |
. |
. |
. |
|
Pasturella multocida |
Abscesses, Wound infection (animal bites), Bacteremia,
Meningitis. |
Penicillin G |
4-6 Mu
daily parenterally |
At
least 2 weeks |
|
Bacteroids species (oral, pharyngeal) |
Oral
disease, Sinusitis, Brain abscess, Lung abscess. |
Penicillin G Clindamycin |
. |
. |
|
Fusobacterium nucleatum |
Ulcerative pharyngitis, Lung abscess, Empyema, Genital
infections, Gingivitis |
Penicillin G Clindamycin Penicillin V |
500 mg every 6 hours |
5 days |
|
Streptobacillus moniliformis |
Bacteremia, Arthritis, Endocarditis, Abscesses. |
Penicillin G |
12-15 Mu per day given parenterally |
3 to
4 weeks |
|
5. Spirochetes
Treponema pallidum |
Syphilis, primary, secondary or latent |
Penicillin G |
20 Mu
daily I.V. |
14 days |
|
|
|
|
followed by 2,4 Mu benzathine Penicillin weekly. |
3 weeks |
|
|
|
|
Infants50 000
units per kg in 2 divided doses per day |
at
least 10 days |
|
Treponema pertenue |
Yaws |
Penicillin G |
. |
. |
|
Leptospira |
Weil's disease, Meningitis. |
Penicillin G Penicillin V or Tetracycline |
Oral
Penicillin 500 mg every 6 hrs |
5 days |
|
6. Actinomycetes
Actinomyces israelii |
Cervicofacial, abdominal, thoracic, and other lesions |
Penicillin G |
10
to 20 Mu daily - I.V. |
6 weeks |
 CONTRA-INDICATIONS:
CONTRA-INDICATIONS:
Must not be administered to patients who are allergic to
penicillins.

WARNINGS:
May cause death when administered to patients sensitive to
penicillins. Do not add to containers of infusions containing
dextrose. It may be piggy-backed via the same administration
set.
DOSAGE AND DIRECTIONS FOR USE:
See table under indications. It should be limited to use by
intravenous route. It can be given as an infusion over 20 to
30 minutes or by constant drip at close intervals (2 to
4 hours). Do not mix with other drugs as it is incompatible with
many. Children should receive 100 000 to 250 000 units/kg per
day in 4 to 6 portions. Newborns up to 1 week - 50 000 to
150 000 units/kg/day in 2 to 3 portions. Dilute with WATER FOR
INJECTIONS. Use only freshly prepared solutions. Discard unused
portion.
|
600 mg (1 Mega-unit) Vial |
3 g (5 Mega-unit) Vial |
|
Concentration |
mL solvent |
Concentration |
mL solvent |
|
100 000 units/mL |
9,6 mL |
250 000 units/ mL |
17,9 mL |
|
200 000 units/mL |
4,6 mL |
400 000 units/ mL |
10,4 mL |
|
250 000 units/mL |
3,6 mL |
500 000 units/ mL |
7,9 mL |
|
500 000 units/2 mL |
3,6 mL |
1 000 000 units/ mL |
2,9 mL |
|
1 000 000 units/mL |
0,6 mL |
2 000 000 units/5 mL |
10,4 mL |
|
1 000 000 units/5 mL |
4,6 mL |
5 000 000 units/5 mL |
2,9 mL |
|
|
|
5 000 000 units/10 mL |
7,9 mL |
SIDE EFFECTS AND SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS:
When administered to a hypersensitive patient, anaphylactic
shock with collapse and sometimes death may occur within
minutes. A generalised sensitivity reaction can occur within
1 to 3 weeks with urticaria, fever, eosinophilia, joint pains,
angioneurotic oedema, erythema multiforme and exfoliative
dermatitis, although an accelerated urticarial reaction can
develop within hours. Glossitis, angular and aphtous stomatitis,
and darkening of the tongue are liable to follow the use of
penicillin.
KNOWN SYMPTOMS OF OVERDOSAGE AND PARTICULARS OF ITS
TREATMENT:
Convulsions and other signs of toxicity to the central
nervous system may occur with very high doses of benzyl
penicillin particularly when administered intravenously to
infants, the elderly, to patients with renal failure, or when
administered intrathecally in doses above 12 mg.
Nephrotoxicity has occurred in some patients with diminished
renal function given large doses of benzyl penicillin. Acute
interstitial nephritis, a hypersensitivity reaction, has also
been reported. Disturbances of blood electrolytes may follow the
administration of large doses of the potassium and sodium salts
of benzyl penicillin.
Treatment:
When cutaneous reactions occur, they may subside
spontaneously with a few hours or days when penicillin is
withdrawn. Control of reactions may be attempted by the
administration of antihistamines or, should there be no response
with corticosteroids. Desensitisation has been attempted when
treatment with penicillin has been considered essential. At the
first sign of an immediate reaction to penicillin treatment,
0,3 to 1 mL of Adrenaline Injection should be given
intramuscularly (or in severe cases 0,2 mL well diluted
intravenously) followed by a further dose if no improvement
occurs. This should be followed by an antihistamine, such as
diphenhydramine or chlorpheniramine, given parenterally and a
corticosteroid given intravenously. If bronchospasm is severe,
aminophylline (250 mg in 10 mL) may be given intravenously.
Assisted respiration is necessary if there is upper airway
obstruction and plasma or suitable electrolyte solutions should
be given intravenously if circulatory failure occurs. Urticaria
and joint pains, if severe, may be treated with corticosteroids
by mouth.
IDENTIFICATION:
Sterile soluble white powder in a clear glass vial.
PRESENTATION:
Benzyl Penicillin 600 mg (1 Mu) Intramed: In boxes of
100 vials each
Benzyl Penicillin 3 g (5 Mu) Intramed: In boxes of 50 vials each
STORAGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Store dry, below 25°C. KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Discard any unused portion.
Any Queries / Know more about Generics
Medicines write us
:
| Information about Generic Medicines |
|
 |
|
|
|
| Information about Manufacturing
|
|
 |
|