| |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ménétrier Disease |
|
|
What is Ménétrier disease?
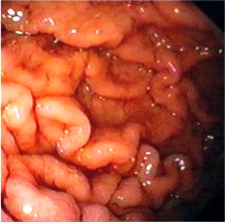
Ménétrier disease causes the ridges along the inside of the
stomach wall—called rugae—to enlarge, forming giant folds in the
lining of the stomach. The rugae enlarge because of an overgrowth
of surface mucous cells of the stomach. In a normal stomach, rugae
release protein-containing mucus. Enlarged rugae release too much
mucus, causing a leakage of protein from the blood into the
stomach. This shortage of protein in the blood is known as
hypoproteinemia. Ménétrier disease also causes a decrease in
stomach acid resulting from a reduction in acid-producing parietal
cells.
People with Ménétrier disease suffer from severe stomach pain,
nausea, frequent vomiting, and other symptoms. They also have a
higher risk of developing stomach cancer, also called gastric
cancer.
Ménétrier disease is also called hypoproteinemic hypertrophic
gastropathy.
Other conditions that can cause enlarged rugae but are not
Ménétrier disease include
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome—a condition in
which tumors in the pancreas cause the stomach to make too much
acid
- syphilis—a type of sexually transmitted
bacterial infection
- cytomegalovirus—a type of viral infection
- histoplasmosis—a type of fungal infection
- linitis plastica—a type of gastric cancer
- gastric lymphoma—a type of cancer originating
in the stomach
What
causes Ménétrier disease?
What causes Ménétrier disease is unclear; however, it is thought
to be an acquired disorder with no known genetic component. Recent
studies suggest people with Ménétrier disease have stomachs that
make abnormally high amounts of a protein called transforming
growth factor-alpha (TGF-α). Growth factors are proteins in the
body that tell cells what to do, such as grow larger, change
shape, or divide to make more cells. A cause for the
overproduction of TGF-α has yet to be found.
How is Ménétrier disease treated?
Treatment may include medications to relieve nausea and pain. A
high-protein diet is prescribed to offset the loss of protein from
enlarged rugae. Part or all of the stomach may need to be removed
if the disease is severe.
The anticancer drug cetuximab (Erbitux) blocks the action of TGF-α
and is being investigated as a promising new treatment for
Ménétrier disease.
|
|
|
|
Ménétrier Disease - treatment of Ménétrier
Disease, Ménétrier Disease types, Disease medicines, Ménétrier Disease
symptoms, Ménétrier Disease and Disease symptoms, Ménétrier Disease symptoms
Disease and diagnosis, Symptoms and Solutions, Signs and Symptoms, type of
Ménétrier Disease, cause common, common Ménétrier Disease, Ménétrier Disease
List, causes list, Infectious Ménétrier Disease, Causes, Diseases , Types,
Prevention, Treatment and Facts, Ménétrier Disease information, Ménétrier
Disease: Definition, Ménétrier Disease names, medical Ménétrier Disease,
medical Ménétrier Disease and disorders, cell Ménétrier Disease, Ménétrier
Disease Worldwide, Ménétrier Disease Research, Ménétrier Disease Control,
Ménétrier Disease Center, Digestive Ménétrier Disease Week, Information
about Ménétrier Disease, causes of different Ménétrier Disease, Ménétrier
Disease Articles, Ménétrier Disease and conditions, Health and Ménétrier
Disease, Ménétrier Disease Patients, Ménétrier Disease and Sciences, causes
of alzheimer's Ménétrier Disease, Ménétrier Disease causes, alternative
medicine heart Ménétrier Disease, body ailments, Ménétrier Disease
medicines, medical antiques, type of blood Ménétrier Disease |
|
|