|
What is Anaemia?
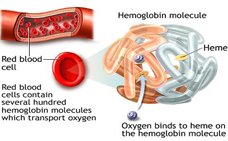
Anaemia is a general term referring to a shortage of red blood
cells or a reduction in their haemoglobin content. Haemoglobin is
the pigment in the blood that carries oxygen in the red blood
cells. A shortage of these red blood cells means that the blood is
unable to carry adequate amounts of oxygen to all parts of the
body. The subsequent reduction in oxygen in the tissues can cause
severe damage.
Good sources of iron include liver, beef, wholemeal bread,
cereals, eggs and dried fruit.
You get anaemia when you don't have enough red blood cells. This
makes it difficult for your blood to carry oxygen, causing unusual
tiredness and other symptoms.
The number of red blood cells can drop if there is:
• a reduction in the number of red blood cells produced
• an increase in the loss of red blood cells.
Red blood cells and oxygen
Term watch
Artery: takes blood from the heart to the body.
Vein: takes blood back to the heart.
Through its pumping action, the heart propels blood around the
body through the arteries.
The red blood cells take up oxygen in the lungs and carry it to
all the body's cells. Your cells use this oxygen to fuel the
combustion (burning) of sugar and fat which produces the body's
energy.
During this process carbon dioxide is created as a waste product.
It binds itself to the red blood cells that have delivered the
oxygen.
The red blood cells then transport the carbon dioxide back to the
lungs. We exchange this carbon dioxide for fresh oxygen by
breathing.
This process is called oxidation.
Why does a lack of iron cause anaemia?
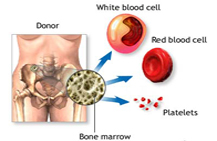
Red blood cells are made in the bone marrow and circulate in the
blood. They only have a life expectancy of about four months.
The body needs iron, vitamin B12 and folic acid (one of the B
group of vitamins) to produce more red blood cells. If there is a
lack of one or more of these nutrients, anaemia will develop.
Iron deficiency anaemia is the most common type of anaemia. In the
UK 8 per cent of women have this type of anaemia.
Iron deficiency is more frequent in women who smoke, eat a diet
low in iron and have heavy periods. It is also common in
vegetarians.
What causes this type of anaemia?
Most childhood cases are caused by a poor diet that contains
little iron.
In adults the most common cause is losing blood faster than the
body can replace it.
• A lack of iron in the diet is common in vegans and vegetarians
because the main dietary source is red meat.
• Babies can develop iron deficiency, especially if they are
premature. Storing iron is not usually completed until the final
stages of pregnancy.
• The body needs more iron when a large amount of cell divisions
occur, such asin pregnancy and during periods of rapid childhood
growth.
• Loss of blood through heavy menstruation can deplete iron
stores.
• Diseases of the small intestine such as gluten intolerance (coeliac
disease) and Crohn's disease (inflammation of the intestine) can
reduce its ability to absorb iron.
• If there seems to be no cause for the iron deficiency, consult
your doctor. Less commonly, small ruptures in the intestine due to
cancer or polyps (small growths), and ulcers in the stomach and
small intestine can cause iron deficiency anaemia. The loss of
blood from the digestive tract may be so slight as to be
undetected on its own.
What are the symptoms of iron-deficiency
anaemia?
If a person is otherwise healthy, it can take some time for the
signs of anaemia to appear.
• The first symptoms will be tiredness and palpitations (awareness
of heartbeat).
• Shortness of breath and dizziness (fainting) are also common.
• If the anaemia is severe, you may experience angina (chest
pain), headache or leg pains (intermittent claudication).
Besides these general symptoms of anaemia,
in pronounced and long-term cases of iron deficiency there may be:
• burning sensation in the tongue
• dryness in the mouth and throat
• sores at the corners of the mouth
• altered sense of touch
• brittle, spoon-shaped nails with vertical stripes and a tendency
to fray
• pica (an insatiable craving for a specific food, eg liquorice)
• brittle hair
• difficulty swallowing.
In rare cases, iron deficiency can cause permanent changes to the
soft lining in the throat (Plummer-Vinson syndrome). This
condition is a preliminary stage to cancer of the oesophagus.
How is anaemia diagnosed?
A blood sample is taken and sent off to the laboratory. An
analysis of the red blood cells is usually included with the
result of the test.
Anaemia in cancer
Anaemia has been reported to affect over 50 percent of cancer
patients. Numerous factors are involved, the most significant of
which are shortened red blood cell life span, blood loss and
suppression of production of red blood cells.
In addition to fatigue, many of the other consequences of
cancer-related anaemia, namely cardiovascular, gastrointestinal
and vascular symptoms, can adversely affect the quality of life of
patients and possibly alter their response to cancer treatment.
Studies have shown that the symptoms of cancer-related anaemia are
exacerbated by commonly used cancer treatments, particularly
platinum-based chemotherapy.
Management of anaemia in cancer
Anaemia in cancer used to be left largely untreated and was
regarded by many physicians as a minor aspect of the disease and
associated therapy. Nowadays, however, recognition of the severity
of the negative impact of anaemia on quality of life, through
fatigue, depression, nausea and the inability of patients to work
or fulfil their social roles, has led to anaemia management
becoming an integral part of quality treatment for cancer
patients.
Previously, blood transfusions were the mainstay of treatment for
cancer-related anaemia. However, approximately 20 percent of blood
transfusions are associated with adverse reactions, some of which
may be severe and/or life threatening. Nowadays recombinant human
erythropoietin (rh-EPO) is used to treat anaemia. Erythropoietin
acts by stimulating the production of red blood cells and
prolonging their survival.
Anaemia in chronic renal disease (renal
anaemia)
Anaemia is extremely common in chronic renal disease (CRD),
affecting up to 90 percent of patients. Renal anaemia is found not
only in patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD) receiving
dialysis treatment, but also in patients who are not yet on
dialysis. One of the most obvious consequences of renal anaemia is
impaired function of the heart and blood vessels (cardiovascular
dysfunction).
Management of renal anaemia
The extent of the devastating consequences of renal anaemia was
not fully revealed until the development of recombinant human
erythropoietin (rh-EPO). Following treatment with rh-EPO, patients
showed improvements in many areas, including physical performance,
contractility of skeletal muscle and overall well being. Nowadays,
rh-EPO together with iron therapy is a standard treatment for
hemodialysis patients with renal anaemia. However, treating renal
anaemia in patients not yet receiving dialysis is extremely
important in order to avoid cardiovascular dysfunction in the long
term.
|