|
Some of the common diseases are :
1) Hepatitis A
- Brief description: It is an
acute but benign form of viral hepatitis caused by RNA virus that
does not persist in the blood serum and is usually transmitted by
taking food or drink that is contaminated with fecal matter
Hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for all travelers to India.
2) Typhoid - Brief
description: It is a serious infection marked by intestinal
inflammation and ulceration; caused by Salmonella typhosa ingested
with food or water. All travelers are recommended to take Typhoid
vaccination.
3) Polio - Brief
description: Poliomyelitis (’polio’) is a viral paralytic
disease. The causative agent, a virus called poliovirus, enters
the body orally, infecting the intestinal lining. It may proceed
to the blood stream and into the central nervous system causing
paralysis and muscle weakness.
To prevent Polio, one-time booster is recommended for any adult
traveler who completed the childhood series but never had polio
vaccine as an adult.
4) Yellow Fever - Brief
description: An acute systemic (bodywide) illness caused by a
virus called Flavivirus. In severe case, the viral infection
causes high fever, bleeding in the skin and necrosis (death) of
cells in the kidney and liver. The damage done to the liver from
the virus results in severe jaundice, which yellows the skin
Vaccination for yellow fever is required only for travelers
arriving from or transiting through any yellow-fever-infected area
like Africa.
5) Japanese Encephalitis -
Brief description: Mosquito-borne viral infection, is the
leading cause of viral encephalitis in Asia. Japanese encephalitis
virus cannot be transmitted from person-to-person.
This vaccine is recommended for travelers staying for more than 1
month and traveling to rural areas or travelers engaging in
extensive unprotected outdoor activities in rural areas,
especially after dusk.
6) Hepatitis B - Brief
description: Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the
liver and can cause both acute and chronic illness.
Travelers who may have intimate contact with local residents
should take this vaccination, especially if their period of stay
is more than six months.
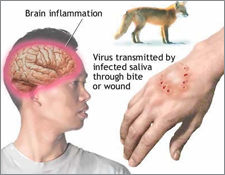
7) Rabies - Brief
description: A viral disease of wild animals that can be
transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected animals such
as dog, cat.
Any traveler who may have direct contact with animals should take
this vaccination.
8) Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) -
Brief description: Measles, also known as rubeola, is a common
disease caused by a virus of the genus Morbillivirus.
If any person born after 1956 has not previously taken this
vaccination, he/she should take two doses of the same.
9) Tetanus-Diphtheria :
Brief description: Tetanus, also called lockjaw, is a medical
condition characterised by a prolonged contraction of skeletal
muscle fibers. Diphtheria is an upper respiratory tract illness
characterised by sore throat, low fever and an adherent membrane
(a pseudomembrane) on the tonsils, pharynx and/or nasal cavity.
You need to take this vaccination every 10 years.
10) Diarrhea - Brief
description: In medicine, diarrhea, also spelt diarrhoea (see
spelling differences), causes frequent loose or liquid bowel
movements
The most common ailment of travelers is diarrhea. The main cause
of the infection is unclean food and water. It is advised to carry
an antibiotic and an anti diarrhea drug if significant diarrhea
occurs. In case of diarrhea, good amount of fluid intake is
required. However, if diarrhea gets severe you should immediately
call a doctor.
11) Malaria - Brief
description: Malaria is a vector-borne infectious disease
caused by protozoan parasites.
Prophylaxis with mefloquine (Lariam), atovaquone/proguanil (Malarone)
or doxycycline is recommended throughout India (including Delhi
and Bombay), except at places located at high altitudes (2000
m/6561 ft). Long-term travelers coming to India may not have
access to medical care all the time; they should bring along
medications for emergency self-treatment in case they develop
symptoms indicative of malaria, such as fever, headaches, chills
and muscle aches. It is important to note that symptoms of malaria
sometimes may not appear for months or even years after exposure.
12) Altitude Sickness: -
Brief description: It also known as acute mountain sickness (AMS),
altitude illness, or soroche, is a pathological condition that is
caused by acute exposure to low air pressure (usually outdoors at
high altitudes).
Altitude sickness may occur to travelers ascending altitudes
greater than 2500m. This specifically includes the mountain areas
of northern India. Those with a history of heart disease, lung
disease or sickle cell disease are advised to avoid high
altitudes.
The above dozen listed diseases seem to be commonly prevalent.The
above is a list of the most common infectious diseases throughout
the world today.
|