| |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Cardiac-Pacemaker |
|
|
What is a
pacemaker? |
 |
|
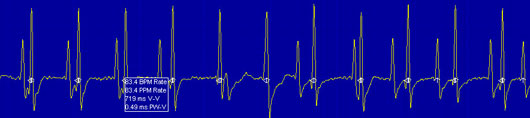
A pacemaker is a man-made device
that controls the heart beats when the heart fails to beat
normally. It is a battery-operated device, about the size of
a matchbox and is placed near the collarbone by a minor
operation. It generates electrical impulses and sends them
to heart through tiny wires. The ends of the wires are
attached to the heart muscle. The wire can also sense the
heart beating normally or abnormally and thus gives signal
to the pacemaker when to start working.
There are many different types of pacemakers to suit various
needs. Some may only help the heart beat when it gets too
slow. Other pacemakers make the heart beat at all times.
Special pacemakers can be used to deliver a shock to the
heart when an abnormal heartbeat occurs. This shock then
corrects irregular heartbeats. Certain advanced type of
pacemakers can even sense the breathing rate. This can be
helpful during exercise, when the breathing rate increases
and the body needs the heart to pump more blood. This makes
a person exercise without getting tired or short of breath.
|
 |
|
When is it
used? |
 |
|
The heart contains a special
electrical system that allows it to beat regularly. But in
certain conditions such as a heart block, the heart may not
beat normally on its own. If the heart rate becomes too
slow, it cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
This causes symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness and
shortness of breath. A pacemaker is used to regulate these
abnormal heartbeats when the condition is serious and is
uncontrolled by drugs.
|
 |
|
How is it
placed in the body? |
 |
|
The patient is given general
anaesthesia or local anaesthesia to numb the area for
surgery. The doctor makes a small cut in the skin over the
upper chest and makes a place for the pacemaker. Then he
places a wire into a vein (a blood vessel carrying impure
blood) and guides one end into the heart and the other end
is connected to the pacemaker.
|
 |
|
What happens
after placing it? |
 |
|
The patient needs to stay in the
hospital for 3-5 days, depending on his condition. The
doctor may check the pacemaker with a monitoring device to
have a baseline or a starting point with which to compare
subsequent checkups. He may also suggest some lifestyle
modifications and the expected or average time before the
battery in the pacemaker may need to be replaced.
|
 |
|
What are the
risks? |
 |
|
There are certain risks involved with the use of a pacemaker
and should be discussed carefully with the doctor. The
doctor will advise a pacemaker only if he finds the need
outweighing the risks; these include:
Infection or bleeding
Wire getting dislodged or breaking
Worsening of other heart problems related to irregular
heart beats
The wire may puncture one of the lungs, the vein or the
heart cavity
A pacemaker, like any other electrical device, may need
replacement if it stops working properly.
|
|
|
Growing Stronger, Growing
Better |
 |
| |
|
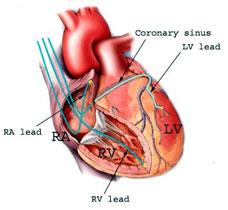
Biventricular Pacemaker
Leads |
| |
 |
|
|
|
Cardiac Laboratory |
| |

|
|
|
Cardiac-Pacemaker - treatment of
Cardiac-Pacemaker, Cardiac-Pacemaker types, Disease medicines,
Cardiac-Pacemaker symptoms, Cardiac-Pacemaker and Disease symptoms,
Cardiac-Pacemaker symptoms Disease and diagnosis, Symptoms and Solutions,
Signs and Symptoms, type of Cardiac-Pacemaker, cause common, common
Cardiac-Pacemaker, Cardiac-Pacemaker List, causes list, Infectious
Cardiac-Pacemaker, Causes, Diseases , Types, Prevention, Treatment and
Facts, Cardiac-Pacemaker information, Cardiac-Pacemaker: Definition,
Cardiac-Pacemaker names, medical Cardiac-Pacemaker, medical
Cardiac-Pacemaker and disorders, cell Cardiac-Pacemaker, Cardiac-Pacemaker
Worldwide, Cardiac-Pacemaker Research, Cardiac-Pacemaker Control,
Cardiac-Pacemaker Center, Digestive Cardiac-Pacemaker Week, Information
about Cardiac-Pacemaker, causes of different Cardiac-Pacemaker,
Cardiac-Pacemaker Articles, Cardiac-Pacemaker and conditions, Health and
Cardiac-Pacemaker, Cardiac-Pacemaker Patients, Cardiac-Pacemaker and
Sciences, causes of alzheimer's Cardiac-Pacemaker, Cardiac-Pacemaker causes,
alternative medicine heart Cardiac-Pacemaker, body ailments,
Cardiac-Pacemaker medicines, medical antiques, type of blood
Cardiac-Pacemaker |
|
|





