|
What are boils?
Boils are painful, pus-filled bumps that form under the skin when
bacteria infect one or more of the hair follicles. Boils usually
start as red, tender lumps. The lumps quickly fill with pus,
growing larger and more painful until they rupture and drain.
Although some boils disappear a few days after they occur, most
take about 2 weeks to heal. Boils can occur anywhere on the skin,
but appear mainly on the face, neck, armpits, buttocks or thighs -
areas where one is most likely to sweat. Sometimes boils occur in
clusters called carbuncles. Although anyone can develop these
painful infections, people in poor general health or with medical
conditions such as acne and diabetes are at increased risk.
What are the symptoms?
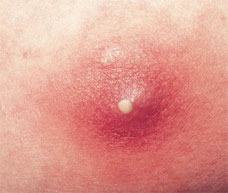
A boil usually appears suddenly as a painful pink or red bump
about 1/2 inch in diameter. The surrounding skin may also be red
and swollen. Within 24 hours, the bump fills with pus. It grows
larger and more painful for 5 to 7 days before it develops a
yellow-white tip that finally ruptures and drains. Boils generally
clear completely in about 2 weeks. Small boils usually heal
without scarring, but a large boil may leave a mark.
What are the causes?
Boils usually form when one or more hair follicles - the
tube-shaped shafts from which hair grows - become infected with
staph bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus). These bacteria, which
normally inhabit the skin and sometimes the throat and nasal
passages, are responsible for a number of serious diseases,
including pneumonia, meningitis, urinary tract infections and
endocarditis - an infection of the lining of the heart. They're
also a major cause of hospital-acquired infections and food borne
illnesses.
Types
of boils
Boils can be of different types based on factors such as infective
organism, location,chronicity, etc. Some of the different boils
include the following:
1)Furuncle;
-
This is an infection within the skin that is
caused by the bacteria Staphylococcusaureus and can be
associated with fever or chills.
2)Cystic acne;
-
This is a boil that occurs when an oil gland
becomes clogged and infected.
-
The deeper skin tissue is affected.
-
More common on the face and is more rampantduring
the teenage years.
3)Hid adenitis suppurative;
-
Boils in this condition tend to occur over the
hairy areas of the body that tendto sweat profusely.
-
More common in the armpits and the groin.
-
Usually requires surgical treatment to remove the
infected sweat glands.
4) Pilonidal cyst
-
The location of these boils is fixed.
-
They occur in the crease of the buttocks, in the
region overlying the tailbone.
-
The boil begins as an infection of a hair
follicle.
-
These boils usually occur following prolonged
sitting or poor hygiene
What are the risk factors?
Although anyone - including otherwise healthy people - can develop
boils, the following factors can increase your risk:
* Poor general health. Having chronic poor health makes it harder
for the immune system to fight infections.
* Diabetes. This disease also makes it more difficult for the body
to fight infection. In fact, recurrent boils sometimes may be a
symptom of diabetes, especially in people older than 40.
* Clothing that are tight. The constant irritation from tight
clothing can cause breaks in the skin, making it easier for
bacteria to enter the body.
* Other skin conditions. Because they damage the skin's protective
barrier, skin problems such as acne and dermatitis make one more
susceptible to boils and carbuncles.
* Immune-suppressing medications. Long-term use of corticosteroids
such as prednisone or other drugs that suppress the immune system
can increase the risk.
What are the complications?
In some cases, bacteria from a boil can enter the bloodstream and
travel to other parts of the body. The spreading infection,
commonly known as blood poisoning (septicaemia), can rapidly
become life-threatening. Initially, blood poisoning causes
symptoms such as chills, a spiking fever, a rapid heart rate and a
feeling of being extremely ill. But the condition can quickly
progress to shock, which is marked by falling blood pressure and
body temperature, confusion, clotting abnormalities and bleeding
into the skin.
What is the treatment?
The doctor may drain a large boil or carbuncle by making a small
incision in the tip. This relieves pain, speeds recovery and helps
lessen scarring. Deep infections that cannot be completely cleared
may be covered with sterile gauze so that the pus can continue to
drain. Sometimes the doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help heal
severe or recurrent infections.
Home care
The following measures may help the infection heal more quickly
and prevent it from spreading:
* Apply a warm cloth to the affected area for approximately 30
minutes every few hours. If possible, soak the cloth in warm
saltwater, which helps the boil rupture and drain more quickly.
* Gently wash the boil twice a day, apply an over-the-counter
antibiotic and cover with a bandage.
* Never squeeze a boil - this can spread the infection.
* Wash your hands thoroughly after treating a boil and clothing
that have touched the infected area.
What is the prevention?
Although it is not always possible to prevent boils, especially if
one has a compromised immune system, the following measures may
help infections:
* Thoroughly clean even small cuts Wash well with soap and apply
an over-the-counter antibiotic ointment
* Avoid constricting clothing Tight clothing should be avoided.
* Eat a healthy diet Eat a healthy diet including whole grains,
fresh fruits and vegetables.
|