 |
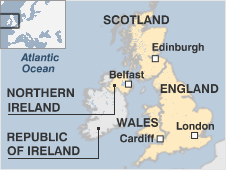
The United Kingdom is made up of England Wales Scotland and Northern Ireland. It has a long history as a major player in international affairs and fulfils an important role in the EU UN and Nato.
The twentieth century saw Britain having to redefine its place in the world. At the beginning of the century it commanded a world-wide empire as the foremost global power.
Two world wars and the end of empire diminished its role but the UK remains a major economic and military power with considerable political and cultural influence around the world.
Overview
Britain was the world's first industrialised country. Its economy remains one of the largest but it has for many years been based on service industries rather than on manufacturing.
Despite being a major member of the EU the country is not part of the euro zone and the question of whether it will join any time soon appears to have receded for the moment. The government has said a series of economic criteria must be met before the issue can be put to a referendum.
In recent years the UK has taken steps to devolve powers to Scotland and Wales. The Scottish Parliament in Edinburgh and the National Assembly for Wales in Cardiff opened in 1999 and the possibility of devolution for the English regions has also been discussed.
In Northern Ireland after decades of violent conflict the Good Friday agreement of 1998 led to a new assembly with devolved powers bringing hopes of lasting peace. The assembly was suspended in 2002 amid a row over alleged IRA activities. Its suspension was to last for three and a half years.
 Palace of Westminster home of the world's oldest parliamentary democracy
|
In a bid to restart the political process and after consultations with Dublin the UK passed legislation paving the way for the recall of the Northern Ireland Assembly in May 2006.
But assembly leaders missed a November deadline to form a power-sharing executive. Assembly elections in the following March led to the eventual swearing-in of the leaders of the power-sharing government on 8 May 2007 ending five years of direct rule from London.
Diversity
The UK is ethnically diverse partly as a legacy of empire. Lately the country has been struggling with issues revolving around multiculturalism immigration and national identity.
This is against a background of concerns about terrorism and political and religious radicalism heightened after the suicide bomb attacks on London's transport network in 2005.
Some politicians and commentators say a stronger sense of shared British values is needed to foster integration within a mixed society. And while some advocate tough policies on limiting immigration others attempt to put the case for it as a positive force.
One of the more recent trends in migration has been the arrival of workers from the new EU member states in Eastern Europe.
Culture
The UK has been at the forefront of youth culture since the heyday of the Beatles and Rolling Stones in the 1960s.
It has a rich literary heritage encompassing the works of English writers such as William Shakespeare and Charles Dickens Scot Robert Burns Welshman Dylan Thomas and Northern Irishman Seamus Heaney.
Traditional music has deep roots across the UK which has also produced classical composers from Henry Purcell in the Baroque period to Benjamin Britten in the 20th century.
Facts
- Full name: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
- Population: 61.6 million (UN 2009)
- Capital: London
- Area: 242514 sq km (93638 sq miles)
- Major language: English
- Major religion: Christianity
- Life expectancy: 77 years (men) 82 years (women) (UN)
- Monetary unit: 1 pound sterling = 100 pence
- Main exports: Manufactured goods chemicals foodstuffs
- GNI per capita: US $45390 (World Bank 2008)
- Internet domain: .uk
- International dialling code: +44
Leaders
Head of state: Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II became queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in 1952 upon the death of her father George VI.

Queen Elizabeth II
|
She is the second longest serving head of state after the Thai King Bhumibol Adulyadej who was crowned in 1946.
She is also head of state of 16 independent countries including Canada and Australia.
As a constitutional monarch her role in the legislative process is largely ceremonial.
Prime minister: Gordon Brown
Gordon Brown became prime minister on 27 June 2007 after serving as Chancellor of the Exchequer (finance minister) in three consecutive Labour governments under Tony Blair. He was the only candidate for the premiership when Mr Blair stood down two years into his third term in office.
 Gordon Brown spent ten years as "prime minister in waiting"
|
The son of a Presbyterian minister Mr Brown was born near the Scottish city of Glasgow in 1951. He was marked out as being academically gifted from an early age and went to Edinburgh University when he was only 16 gaining a first-class degree in history.
He joined the Labour Party while still at university and after graduating became a politics lecturer. He rose rapidly through the ranks of the party inspiring fierce loyalty in those close to him.
In 1992 he was appointed shadow chancellor. On the Labour Party's landslide election victory in 1997 - after 18 years in opposition - he assumed the chancellorship holding the post for a record 10 years during which Britain enjoyed an unprecedented era of sustained economic growth. His avowed commitment to fiscal prudence earned him the nickname "the Iron Chancellor".
However Mr Brown's reputation for financial responsibility has been questioned in the wake of the global financial crisis which struck in 2008 a crisis which has seen the British economy hit hard.
Opposition politicians have taken delight in reminding him of his oft-repeated assertion that under a Labour government there would be no return to "boom and bust" economics. In his defence Mr Brown has argued that the steps taken by Britain to address the crisis have been copied by governments around the world.
 Tony Blair the first Labour leader to serve three terms
|
In the foreign policy arena Mr Brown is regarded as more of an Atlanticist than a Europhile. He has also been long committed to increasing aid to Africa.
He faces the challenge of restoring the British people's confidence in a Labour government before the next general election due in a few years' time.
- Chancellor of the Exchequer: Alistair Darling
- Home Secretary: Alan Johnson
- Foreign Secretary: David Miliband
Media
The UK has a strong tradition of public-service broadcasting and an international reputation for creative programme-making.
The fledgling BBC began daily radio broadcasts in 1922 and quickly came to play a pivotal role in national life. The Empire Service - the forerunner of the BBC World Service - established a reputation worldwide. The BBC is funded by a licence fee which all households with a TV set must pay.
 BBC Broadcasting House a London landmark
|
Commercial TV began in 1955 with the launch of ITV. Commercial radio was introduced in the 1970s although ship-based pirate radio stations flourished in the 1960s before being outlawed. Hundreds of privately-owned radio and TV stations now compete with the BBC for listeners and viewers.
Home-grown soap operas have long topped the TV ratings and British viewers keenly follow the ups and downs of life in east London's Albert Square the setting for the BBC's EastEnders and Coronation Street - ITV's soap about northern-English working-class life. Programmes which catapult ordinary people into the public eye - known as reality TV - are enjoying a wave of popularity.
In a rapidly-changing digital world British media providers are looking at new ways of reaching audiences via computers and personal multimedia devices.
The once-dominant terrestrial TV networks face strong competition from digital satellite and cable which offer hundreds of channels and digital
terrestrial TV which carries a smaller number of mainly free-to-view channels. By August 2008 digital TV was in 87% of British homes. Digital radio (DAB) has had a slower start but the BBC and commercial operators provide digital-only radio services.
Britain's media regulator Ofcom has set a timetable for a switchover from analogue to digital TV broadcasting; it hopes to turn off the analogue TV signal by 2012.
The British media are free and able to report on all aspects of British life. The variety of publications reflects the full spectrum of political opinion as well as the British public's voracious appetite for newspapers.
The press
- The Daily Telegraph - broadsheet
- Financial Times - daily business broadsheet
- The Guardian - daily former broadsheet
- The Independent - daily former broadsheet
- The Times - daily former broadsheet
- The Sun - daily tabloid
- The Mirror - daily tabloid
- The Daily Mail - tabloid
- The Daily Express - daily tabloid
- The Scotsman - Scottish daily
- Western Mail - Welsh daily
Television
- BBC TV - operates BBC1 BBC2 and digital services including BBC News channel
- BBC World News - commercially-funded international news channel
- ITV - major commercial network organised around regional franchises
- Channel 4 - commercially funded but publicly owned national station
- five - national commercial channel
- Independent Television News (ITN) - supplier of news to ITV Channel 4
- British Sky Broadcasting (BSkyB) - operator of digital satellite platform Sky and provider of film entertainment channels and news channel Sky News
Radio
- BBC Radio - national services include new-music station Radio 1 adult music station Radio 2 cultural network Radio 3 flagship speech station Radio 4 and news and sport station Five Live
- BBC Radio Scotland
- BBC Radio nan Gaidheal - Gaelic-language station for Scotland
- BBC Radio Ulster - for Northern Ireland
- BBC Radio Wales
- BBC Radio Cymru - Welsh-language
- BBC Asian Network - for Asian communities in the UK
- BBC World Service - major international broadcaster heard worldwide via shortwave and increasingly on FM relays programmes in more than 30 languages
- Absolute Radio - national commercial pop and rock station
- Talk Sport - national commercial sports station
- Classic FM - national commercial classical music station
News agency
-
The Press Association
AFRICA | ASIA-PACIFIC | AMERICAS | EUROPE | MIDDLEEAST | SOUTHASIA
Mauritania Mauritius Morocco Mozambique Namibia Niger Nigeria Republic-of-congo Rwanda Sao-tome-and-principe Senegal Seychelles Sierra-leone Somalia South-africa Sudan Swaziland Tanzania The-gambia Togo Tunisia Uganda zambia Zimbabwe Australia Brunei Burma Cambodia China East-timor Fiji Indonesia Japan Kazakhstan Kiribati Kyrgyzstan Laos Malaysia Marshall-islands Micronesia Mongolia Nauru New-zealand North-korea Palau Papua-new-guinea Samoa Singapore Solomon-islands South-korea Taiwan Tajikistan Thailand The-philippines Tonga Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vietnam Antigua-and-barbuda Argentina Bahamas Barbados Belize Bolivia Brazil Canada Chile Colombia Costa-rica Cuba Dominica Dominican-republic Ecuador El-salvador Grenada Guatemala GuyanaHaiti Honduras Jamaica Mexico Nicaragua Panama Paraguay Peru St-kitts-and-nevis St-lucia St-vincent-and-the-grenadines Suriname Trinidad-and-tobago United-states-of-america Uruguay Venezuela Albania Andorra Armenia Austria Azerbaijan Belarus Belgium Bosnia-hercegovina Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Czech-republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Georgia Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Italy Latvia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macedonia Malta Moldova Monaco Montenegro Norway Poland Portugal Russia San-marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland The-netherlands Turkey Ukraine United-kingdom Vatican Algeria Egypt Iran Iraq Israel-and-palestinian-territories Jordan Kuwait Lebanon Libya Mauritania Oman Saudi-arabia Sudan Syria Tunisia United-arab-emirates Yemen Afghanistan Bangladesh Bhutan India Nepal Pakistan Sri-Lanka The-Maldives

