|
|
REMATAL® CII Sodium Solution
(pentobarbital sodium injection, USP)
REMATAL® (pentobarbital
sodium injection, USP)
Rx only CII
Vials
DO NOT USE IF MATERIAL HAS PRECIPITATED
• REMATAL® is a member of the barbiturate class of medications.
• REMATAL® is a sterile solution for intravenous or
intramuscular injection in 20 mL and 50 mL multiple-dose vials.
Indication
REMATAL® (pentobarbital sodium injection, USP) is indicated for
use as a sedative, a hypnotic for short-term treatment of
insomnia, preanaesthetic and as an anticonvulsant in the
emergency control of certain acute convulsive episodes, such as
those associated with status epilepticus, cholera, eclampsia,
meningitis, tetanus and toxic reactions to strychinne or local
anesthetics.
Important Safety Information
REMATAL is contraindicated in patients with a known
hypersensitivity to any barbiturate,.jpg) manifest
or latent porphyria. Barbiturates including REMATAL may be habit
forming. Abrupt discontinuation may result in withdrawal
symptoms, including delirium, convulsions and possibly death.
Too rapid of an intravenous administration may cause respiratory
depression, apnea, laryngospasm, or vasodilation with fall in
blood pressure. manifest
or latent porphyria. Barbiturates including REMATAL may be habit
forming. Abrupt discontinuation may result in withdrawal
symptoms, including delirium, convulsions and possibly death.
Too rapid of an intravenous administration may cause respiratory
depression, apnea, laryngospasm, or vasodilation with fall in
blood pressure.
Concomitant use of alcohol or other CNS depressants may produce
additive CNS depressant effects. Barbiturates should be
administered with caution, if at all, to patients who are
mentally depressed, have suicidal tendencies, chronic or acute
pain. Barbiturates can cause fetal damage and infants may have
withdrawal symptoms if mothers receive barbiturates. Withdrawal
symptoms occur in infants born to mothers who receive
barbiturates during the last trimester of pregnancy. Prolonged
treatment with barbiturates should be monitored.
The most commonly reported adverse event (>1 in 100 patients)
is somnolence.
Each mL contains:
Pentobarbital Sodium, derivative of barbituric
acid.......................................50 mg
Propylene
glycol........................................................................................
40% v/v
Alcohol............................................................................................................
10%
Water for
Injection..............................................................................................
qs
(pH adjusted to approximately 9.5 with
hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.)
Vial stoppers are latex free.
HOW SUPPLIED
REMATAL® Sodium Solution (pentobarbital sodium injection, USP)
is available in the following sizes:
20-mL multiple-dose vial, 1 g per vial (TPL 6734-501-322); and
50-mL multiple-dose.jpg)
Exposure of pharmaceutical products to heat should be minimized.
Avoid excessive heat. Protect from freezing. It is recommended
that the product be stored at 20-25◦C (68-77◦F), however, brief
excursions are permitted between 15-30◦C (59-86◦F). See USP
controlled room temperature.
Inspection: Parenteral drug products should be inspected
visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to
administration, whenever solution containers permit. Solutions
for injection showing evidence of precipitation should not be
used.
There is no average intravenous dose of REMATAL® Sodium Solution
(pentobarbital sodium injection) that can be relied on to
produce similar effects in different patients. The possibility
of overdose and respiratory depression is remote when the drug
is injected slowly in fractional doses.
A commonly used initial dose for the 70 kg adult is 100 mg.
Proportional reduction in dosage should be made for pediatric or
debilitated patients. At least one minute is necessary to
determine the full effect of intravenous pentobarbital. If
necessary, additional small increments of the drug may be given
up to a total of from 200 to 500 mg for normal adults.
Anticonvulsant use: In convulsive states, dosage of REMATAL®
Sodium Solution should be kept to a minimum to avoid compounding
the depression which may follow convulsions. The injection must
be made slowly with due regard to the time required for the drug
to penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
Intravenous Administration: REMATAL®L Sodium Solution should not
be admixed with any other medication or solution. IV injection
is restricted to conditions in which other routes are not
feasible, either because the patient is unconscious (as in
cerebral hemorrhage, eclampsia, or status epilepticus), or
because the patient resists (as in delirium), or because prompt
action is imperative. Slow IV injection is essential, and
patients should be carefully observed during administration.
This requires that blood pressure, respiration, and cardiac
function be maintained, vital signs be recorded, and equipment
for resuscitation and artificial ventilation be available. The
rate of IV injection should not exceed 50 mg/min for
pentobarbital sodium.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
.jpg)
Dosages of barbiturates must be individualized with full
knowledge of their particular characteristics and recommended
rate of administration. Factors of consideration are the
patient’s age, weight, and condition. Parenteral routes should
be used only when oral administration is impossible or
impractical.
Intramuscular Administration: IM injection of the sodium salts
of barbiturates should be made deeply into a large muscle, and a
volume of 5 mL should not be exceeded at any one site because of
possible tissue irritation. After IM injection of a hypnotic
dose, the patient’s vital signs should be monitored. The usual
adult dosage of REMATAL® Sodium Solution is 150 to 200 mg as a
single IM injection; the recommended pediatric dosage ranges
from 2 to 6 mg/kg as a single IM injection not to exceed 100 mg.
DESCRIPTION
The barbiturates are nonselective central nervous system
depressants which are primarily used as sedative hypnotics and
also anticonvulsants in subhypnotic doses. The barbiturates and
their sodium salts are subject to control under the Federal
Controlled Substances Act (See “Drug Abuse and Dependence”
section).
The sodium salts of amobarbital, pentobarbital, phenobarbital,
and secobarbital are available as sterile parenteral solutions.
Barbiturates are substituted pyrimidine derivatives in which the
basic structure common to these drugs is barbituric acid, a
substance which has no central nervous system (CNS) activity.
CNS activity is obtained by substituting alkyl, alkenyl, or aryl
groups on the pyrimidine ring.
REMATAL® Sodium Solution (pentobarbital sodium injection) is a
sterile solution for intravenous or intramuscular injection.
Each mL contains pentobarbital sodium 50 mg, in a vehicle of
propylene glycol, 40%, alcohol, 10% and water for injection, to
volume. The pH is adjusted to approximately 9.5 with
hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.
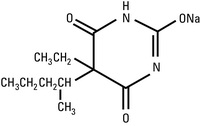
REMATAL® Sodium is a short-acting barbiturate, chemically
designated as sodium 5-ethyl-5-(1-methylbutyl) barbiturate. The
structural formula for pentobarbital sodium is:
The sodium salt occurs as a white, slightly bitter powder which
is freely soluble in water and alcohol but practically insoluble
in benzene and ether.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Barbiturates are capable of producing all levels of CNS mood
alteration from excitation to mild sedation, to hypnosis, and
deep coma. Overdosage can produce death. In high enough
therapeutic doses, barbiturates induce anesthesia.
Barbiturates depress the sensory cortex, decrease motor
activity, alter cerebellar function, and produce drowsiness,
sedation, and hypnosis.
Barbiturate-induced sleep differs from physiological sleep.
Sleep laboratory
.jpg) studies
have demonstrated that barbiturates reduce the amount of time
spent in the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep or dreaming
stage. Also, Stages III and IV sleep are decreased. Following
abrupt cessation of barbiturates used regularly, patients may
experience markedly increased dreaming, nightmares, and/or
insomnia. Therefore, withdrawal of a single therapeutic dose
over 5 or 6 days has been recommended to lessen the REM rebound
and disturbed sleep which contribute to drug withdrawal syndrome
(for example, decrease the dose from 3 to 2 doses a day for 1
week). studies
have demonstrated that barbiturates reduce the amount of time
spent in the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep or dreaming
stage. Also, Stages III and IV sleep are decreased. Following
abrupt cessation of barbiturates used regularly, patients may
experience markedly increased dreaming, nightmares, and/or
insomnia. Therefore, withdrawal of a single therapeutic dose
over 5 or 6 days has been recommended to lessen the REM rebound
and disturbed sleep which contribute to drug withdrawal syndrome
(for example, decrease the dose from 3 to 2 doses a day for 1
week).
In studies, secobarbital sodium and pentobarbital sodium have
been found to lose most of their effectiveness for both inducing
and maintaining sleep by the end of 2 weeks of continued drug
administration at fixed doses. The short-, intermediate-, and,
to a lesser degree, long-acting barbiturates have been widely
prescribed for treating insomnia. Although the clinical
literature abounds with claims that the short-acting
barbiturates are superior for producing sleep while the
intermediate-acting compounds are more effective in maintaining
sleep, controlled studies have failed to demonstrate these
differential effects. Therefore, as sleep medications, the
barbiturates are of limited value beyond short-term use.
Barbiturates have little analgesic action at subanesthetic
doses. Rather, in subanesthetic doses these drugs may increase
the reaction to painful stimuli. All barbiturates exhibit
anticonvulsant activity in anesthetic doses. However, of the
drugs in this class, only phenobarbital, mephobarbital, and
metharbital have been clinically demonstrated to be effective as
oral anticonvulsants in subhypnotic doses.
Barbiturates are respiratory depressants. The degree of
respiratory depression is dependent upon dose. With hypnotic
doses, respiratory depression produced by barbiturates is
similar to that which occurs during physiologic sleep with
slight decrease in blood pressure and heart rate.
Studies in laboratory animals have shown that barbiturates cause
reduction in the tone and contractility of the uterus, ureters,
and urinary bladder. However, concentrations of the drugs
required to produce this effect in humans are not reached with
sedative-hypnotic doses.
Barbiturates do not impair normal hepatic function, but have
been shown to induce liver microsomal enzymes, thus increasing
and/or altering the metabolism of barbiturates and other drugs.
Pharmacokinetics:
Barbiturates are absorbed in varying degrees following oral,
rectal, or parenteral administration. The salts are more rapidly
absorbed than are the acids.
The onset of action for oral or rectal administration varies
from 20 to 60 minutes. For IM administration, the onset of
action is slightly faster. Following IV administration, the
onset of action ranges from almost immediately for pentobarbital
sodium to 5 minutes for phenobarbital sodium. Maximal CNS
depression may not occur until 15 minutes or more after IV
administration for phenobarbital sodium.
Duration of action, which is related to the rate at which the
barbiturates are redistributed throughout the body, varies among
persons and in the same person from time to time.
No studies have demonstrated that the different routes of
administration are equivalent with respect to bioavailability.
Barbiturates are weak acids that are absorbed and rapidly
distributed to all tissues and fluids with high concentrations
in the brain, liver, and kidneys. Lipid solubility of the
barbiturates is the dominant factor in their distribution within
the body. The more lipid soluble the barbiturate, the more
rapidly it penetrates all tissues of the body. Barbiturates are
bound to plasma and tissue proteins to a varying degree with the
degree of binding increasing directly as a function of lipid
solubility.
Phenobarbital has the lowest lipid solubility, lowest plasma
binding, lowest brain protein binding, the longest delay in
onset of activity, and the longest duration of action. At the
opposite extreme is secobarbital which has the highest lipid
solubility, plasma protein binding, brain protein binding, the
shortest delay in onset of activity, and the shortest duration
of action. Butabarbital is classified as an intermediate
barbiturate.
The plasma half-life for pentobarbital in adults is 15 to 50
hours and appears to be dose dependent.
Barbiturates are metabolized primarily by the hepatic microsomal
enzyme system, and the metabolic products are excreted in the
urine, and less commonly, in the feces. Approximately 25 to 50
percent of a dose of aprobarbital or phenobarbital is eliminated
unchanged in the urine, whereas the amount of other barbiturates
excreted unchanged in the urine is negligible. The excretion of
unmetabolized barbiturate is one feature that distinguishes the
long-acting category from those belonging to other categories
which are almost entirely metabolized. The inactive metabolites
of the barbiturates are excreted as conjugates of glucuronic
acid.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Parenteral:
a. Sedatives.
b. Hypnotics, for the short-term treatment of insomnia, since
they appear to lose their effectiveness for sleep induction and
sleep maintenance after 2 weeks (See “Clinical Pharmacology”
section).
c. Preanesthetics.
d. Anticonvulsant, in anesthetic doses, in the emergency control
of certain acute convulsive episodes, e.g., those associated
with status epilepticus, cholera, eclampsia, meningitis,
tetanus, and toxic reactions to strychnine or local anesthetics.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Barbiturates are contraindicated in patients with known
barbiturate sensitivity. Barbiturates are also contraindicated
in patients with a history of manifest or latent porphyria.
WARNINGS
1. Habit forming: Barbiturates may be habit forming. Tolerance,
psychological and
 physical
dependence may occur with continued use. (See “Drug Abuse and
Dependence” and “Pharmacokinetics” sections). Patients who have
psychological dependence on barbiturates may increase the dosage
or decrease the dosage interval without consulting a physician
and may subsequently develop a physical dependence on
barbiturates. To minimize the possibility of overdosage or the
development of dependence, the prescribing and dispensing of
sedative-hypnotic barbiturates should be limited to the amount
required for the interval until the next appointment. Abrupt
cessation after prolonged use in the dependent person may result
in withdrawal symptoms, including delirium, convulsions, and
possibly death. Barbiturates should be withdrawn gradually from
any patient known to be taking excessive dosage over long
periods of time. (See “Drug Abuse and Dependence” section). physical
dependence may occur with continued use. (See “Drug Abuse and
Dependence” and “Pharmacokinetics” sections). Patients who have
psychological dependence on barbiturates may increase the dosage
or decrease the dosage interval without consulting a physician
and may subsequently develop a physical dependence on
barbiturates. To minimize the possibility of overdosage or the
development of dependence, the prescribing and dispensing of
sedative-hypnotic barbiturates should be limited to the amount
required for the interval until the next appointment. Abrupt
cessation after prolonged use in the dependent person may result
in withdrawal symptoms, including delirium, convulsions, and
possibly death. Barbiturates should be withdrawn gradually from
any patient known to be taking excessive dosage over long
periods of time. (See “Drug Abuse and Dependence” section).
2. IV administration: Too rapid administration may cause
respiratory depression, apnea, laryngospasm, or vasodilation
with fall in blood pressure.
3. Acute or chronic pain: Caution should be exercised when
barbiturates are administered to patients with acute or chronic
pain, because paradoxical excitement could be induced or
important symptoms could be masked. However, the use of
barbiturates as sedatives in the postoperative surgical period
and as adjuncts to cancer chemotherapy is well established.
4. Use in pregnancy: Barbiturates can cause fetal damage when
administered to a pregnant woman. Retrospective, case-controlled
studies have suggested a connection between the maternal
consumption of barbiturates and a higher than expected incidence
of fetal abnormalities. Following oral or parenteral
administration, barbiturates readily cross the placental barrier
and are distributed throughout fetal tissues with highest
concentrations found in the placenta, fetal liver, and brain.
Fetal blood levels approach maternal blood levels following
parenteral administration.
Withdrawal symptoms occur in infants born to mothers who receive
barbiturates throughout the last trimester of pregnancy. (See
“Drug Abuse and Dependence” section). If this drug is used
during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while
taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the
potential hazard to the fetus.
5. Synergistic effects: The concomitant use of alcohol or other
CNS depressants may produce additive CNS depressant effects.
PRECAUTIONS
General: Barbiturates may be habit forming. Tolerance and
psychological and physical dependence may occur with continuing
use. (See “Drug Abuse and Dependence” section). Barbiturates
should be administered with caution, if at all, to patients who
are mentally depressed, have suicidal tendencies, or a history
of drug abuse.
Elderly or debilitated patients may react to barbiturates with
marked excitement, depression, and confusion. In some persons,
barbiturates repeatedly produce excitement rather than
depression.
In patients with hepatic damage, barbiturates should be
administered with caution and initially in reduced doses.
Barbiturates should not be administered to patients showing the
premonitory signs of hepatic coma.
Parenteral solutions of barbiturates are highly alkaline.
Therefore, extreme care should be taken to avoid perivascular
extravasation or intra-arterial injection. Extravascular
injection may cause local tissue damage with subsequent
necrosis; consequences of intra-arterial injection may vary from
transient pain to gangrene of the limb. Any complaint of pain in
the limb warrants stopping the injection.
Information for the patient:
Practitioners should give the following information and
instructions to patients receiving barbiturates.
1. The use of barbiturates carries with it an associated risk of
psychological and/or physical dependence. The patient should be
warned against increasing the dose of the drug without
consulting a physician.
2. Barbiturates may impair mental and/or physical abilities
required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks
(e.g., driving, operating machinery, etc.).
3. Alcohol should not be consumed while taking barbiturates.
Concurrent use of the barbiturates with other CNS depressants
(e.g., alcohol, narcotics,

|
|
|

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg) manifest
or latent porphyria. Barbiturates including REMATAL may be habit
forming. Abrupt discontinuation may result in withdrawal
symptoms, including delirium, convulsions and possibly death.
Too rapid of an intravenous administration may cause respiratory
depression, apnea, laryngospasm, or vasodilation with fall in
blood pressure.
manifest
or latent porphyria. Barbiturates including REMATAL may be habit
forming. Abrupt discontinuation may result in withdrawal
symptoms, including delirium, convulsions and possibly death.
Too rapid of an intravenous administration may cause respiratory
depression, apnea, laryngospasm, or vasodilation with fall in
blood pressure..jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) studies
have demonstrated that barbiturates reduce the amount of time
spent in the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep or dreaming
stage. Also, Stages III and IV sleep are decreased. Following
abrupt cessation of barbiturates used regularly, patients may
experience markedly increased dreaming, nightmares, and/or
insomnia. Therefore, withdrawal of a single therapeutic dose
over 5 or 6 days has been recommended to lessen the REM rebound
and disturbed sleep which contribute to drug withdrawal syndrome
(for example, decrease the dose from 3 to 2 doses a day for 1
week).
studies
have demonstrated that barbiturates reduce the amount of time
spent in the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep or dreaming
stage. Also, Stages III and IV sleep are decreased. Following
abrupt cessation of barbiturates used regularly, patients may
experience markedly increased dreaming, nightmares, and/or
insomnia. Therefore, withdrawal of a single therapeutic dose
over 5 or 6 days has been recommended to lessen the REM rebound
and disturbed sleep which contribute to drug withdrawal syndrome
(for example, decrease the dose from 3 to 2 doses a day for 1
week).  physical
dependence may occur with continued use. (See “Drug Abuse and
Dependence” and “Pharmacokinetics” sections). Patients who have
psychological dependence on barbiturates may increase the dosage
or decrease the dosage interval without consulting a physician
and may subsequently develop a physical dependence on
barbiturates. To minimize the possibility of overdosage or the
development of dependence, the prescribing and dispensing of
sedative-hypnotic barbiturates should be limited to the amount
required for the interval until the next appointment. Abrupt
cessation after prolonged use in the dependent person may result
in withdrawal symptoms, including delirium, convulsions, and
possibly death. Barbiturates should be withdrawn gradually from
any patient known to be taking excessive dosage over long
periods of time. (See “Drug Abuse and Dependence” section).
physical
dependence may occur with continued use. (See “Drug Abuse and
Dependence” and “Pharmacokinetics” sections). Patients who have
psychological dependence on barbiturates may increase the dosage
or decrease the dosage interval without consulting a physician
and may subsequently develop a physical dependence on
barbiturates. To minimize the possibility of overdosage or the
development of dependence, the prescribing and dispensing of
sedative-hypnotic barbiturates should be limited to the amount
required for the interval until the next appointment. Abrupt
cessation after prolonged use in the dependent person may result
in withdrawal symptoms, including delirium, convulsions, and
possibly death. Barbiturates should be withdrawn gradually from
any patient known to be taking excessive dosage over long
periods of time. (See “Drug Abuse and Dependence” section). .jpg)
.png)
.jpg)