|
|
Bisoprolol 2.5 mg film coated tablet
Bisoprolol 5 mg film coated tablet
Bisoprolol 10 mg film coated tablet
TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION
TREATMENT OF STABLE CHRONIC ANGINA
TREATMENT OF STABLE CHRONIC HEART FAILURE WITH REDUCED SYSTOLIC
LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION IN ADDITION TO ACE INHIBITORS, AND
DIURETICS, AND OPTIONALLY CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES
Inactive ingredients include Colloidal Silicon Dioxide,
Corn Starch, Dibasic Calcium Phosphate, Hypromellose, Magnesium
Stearate, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Polyethylene Glycol,
Polysorbate 80, and Titanium Dioxide. The 5 mg/6.25 mg tablet also
contains Red and Yellow Iron Oxide. The 2.5 mg/6.25 mg tablet also
contains Crospovidone, Pregelatinized Starch, and Yellow Iron
Oxide.
INDICATIONS
Cadrol (bisoprolol fumarate and hydrochlorothiazide) is indicated
in the management of hypertension. It combines two
antihypertensive agents in a once-daily dosage: a synthetic
beta1-selective (cardioselective) adrenoceptor blocking agent (bisoprolol
fumarate) and a benzothiadiazine diuretic (hydrochlorothiazide).
USES
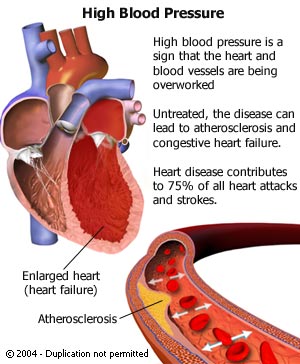
This combination medication is used to treat high blood pressure
(hypertension). Lowering high blood pressure helps prevent
strokes, heart attacks, and kidney problems.
This product contains two medications. Bisoprolol is a beta
blocker that works by blocking the effect of certain natural
chemicals (e.g., epinephrine) on the heart and blood vessels. This
slows your heartbeat, lowers blood pressure, and reduces strain on
the heart. Hydrochlorothiazide is a "water pill" (diuretic) that
works by increasing the amount of urine that you make. This causes
your body to get rid of extra salt and water, which probably helps
to relax the blood vessels so that blood can flow more easily.
These two drugs are used together when one medication is not
controlling your blood pressure. Using these two drugs together
can also reduce the amount of each drug you must take, thereby
decreasing the chances of side effects.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Bisoprolol is an effective treatment of hypertension in once-daily
doses of 2.5 to 40 mg, while hydrochlorothiazide is effective in
doses of 12.5 to 50 mg. In clinical trials of bisoprolol/hydrochlorothiazide
combination therapy using bisoprolol doses of 2.5 to 20 mg and
hydrochlorothiazide doses of 6.25 to 25 mg, the antihypertensive
effects increased with increasing doses of either component.
WARNINGS
Cardiac Failure: In general, beta-blocking agents should be
avoided in patients with overt congestive failure. However, in
some patients with compensated cardiac failure, it may be
necessary to utilize these agents. In such situations, they must
be used cautiously.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Electrolyte and Fluid Balance Status: Although the probability of
developing hypokalemia is reduced with Cadrol because of the very
low dose of HCTZ employed, periodic determination of serum
electrolytes should be performed, and patients should be observed
for signs of fluid or electrolyte disturbances, ie, hyponatremia,
hypochloremic alkalosis, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia.
Thiazides have been shown to increase the urinary excretion of
magnesium; this may result in hypomagnesemia.
Administration: For oral use.
Bisoprolol fumarate tablet should be taken in morning and can be
taken with food in morning. They should be swallowed in liquid
and should not be chewed.
Treatment of hypertension and chronic stable angina pectoris
Adults
The dosage should be individually adjusted. It is recommended to
start with 5 mg per day. The usual dose is 10 mg once daily with
a maximum recommended dose of 20 mg per day.
Patients with renal impairment
In patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <
20 ml/min) the dose should not exceed 10 mg once daily. This
dosage may eventually be divided into halves.
Patients with severe liver impairment
No dosage adjustment is required, however careful monitoring is
advised.
Elderly
No dosage adjustment is normally required. It is recommended to
start with the lowest possible dose.
Children
There is no experience with bisoprolol in children, therefore
its use cannot be recommended for children.
Discontinuation of treatment
Treatment should not be stopped abruptly (see section 4.4). The
dosage should be diminished slowly by a weekly halving of the
dose.
Treatment of stable chronic heart failure
Adults
Standard treatment of CHF consists of an ACE inhibitor (or an
angiotensin receptor blocker in case of intolerance to ACE
inhibitors), a beta-blocker, diuretics, and when appropriate
cardiac glycosides. Patients should be stable (without acute
failure) when bisoprolol treatment is initiated.
It is recommended that the treating physician should be
experienced in the management of chronic heart failure.
Transient worsening of heart failure, hypotension, or
bradycardia may occur during the titration period and
thereafter.
Titration phase
The treatment of stable chronic heart failure with bisoprolol
requires a titration phase
The treatment with bisoprolol is to be started with a gradual
uptitration according to the following steps:
- 1.25 mg once daily for 1 week, if well tolerated increase
to
- 2.5 mg once daily for a further week, if well tolerated
increase to
- 3.75 mg once daily for a further week, if well tolerated
increase to
- 5 mg once daily for the 4 following weeks, if well tolerated
increase to
- 7.5 mg once daily for the 4 following weeks, if well tolerated
increase to
- 10 mg once daily for the maintenance therapy.
The maximum recommended dose is 10 mg once daily.
Close monitoring of vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure) and
symptoms of worsening heart failure is recommended during the
titration phase. Symptoms may already occur within the first day
after initiating the therapy.
Treatment modification
If the maximum recommended dose is not well tolerated, gradual
dose reduction may be considered.
In case of transient worsening of heart failure, hypotension, or
bradycardia reconsideration of the dosage of the concomitant
medication is recommended. It may also be necessary to
temporarily lower the dose of bisoprolol or to consider
discontinuation.
The reintroduction and/or uptitration of bisoprolol should
always be considered when the patient becomes stable again.
If discontinuation is considered, gradual dose decrease is
recommended, since abrupt withdrawal may lead to acute
deterioration of the patient's condition.
Treatment of stable chronic heart failure with bisoprolol is
generally a long-term treatment.
Special population
Renal or hepatic impairment
There is no information regarding pharmacokinetics of bisoprolol
in patients with chronic heart failure and with impaired hepatic
or renal function. Up titration of the dose in these populations
should therefore be made with additional caution.
Elderly
No dosage adjustment is normally required.
Children`
There is no paediatric experience with bisoprolol, therefore its
use cannot be recommended for children
Parathyroid Disease
Calcium excretion is decreased by thiazides, and pathologic
changes in the parathyroid glands, with hypercalcemia and
hypophosphatemia, have been observed in a few patients on
prolonged thiazide therapy.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Cadrol is contraindicated in patients in cardiogenic shock, overt
cardiac failure (see WARNINGS), second or third degree AV block,
marked sinus bradycardia, anuria, and hypersensitivity to either
component of this product or to other sulfonamide-derived drugs.
Presentation
Cadrol
Tablets
Blister of 10 Tablets
Nature and contents of container
PVC/PVDC-Alu Blister or ALU-ALU Blister in
Pack sizes of 20, 28, 30, 50, 56, 60, 90 and 100 tablets.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
|
|





.png)